RND
Published:
RND
Implementation of RND reinforcement learning algorithm
Technical Details
- Framework: PyTorch
- Environment: LunarLander
- Category: Exploration Methods
This directory contains implementations of Random Network Distillation (RND) combined with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) for cur### FrozenLake-v1 (8x8 Map)
The following demonstrates RND performance on the challenging FrozenLake 8x8 environment with 64 states:
Agent gameplay demonstration:
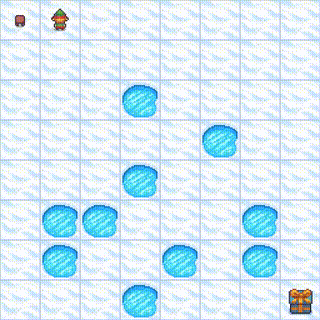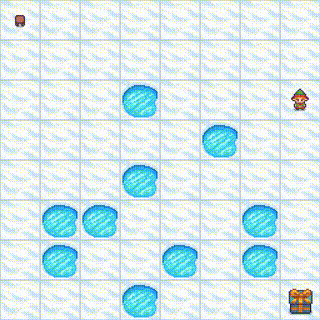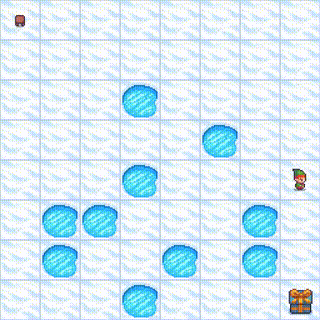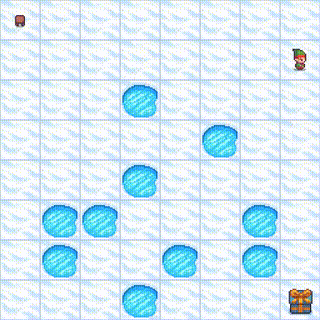
Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: FrozenLake 8x8 is a significantly more challenging environment than the standard 4x4 version, with 64 discrete states instead of 16. The stochastic slippery dynamics make exploration particularly difficult, as the agent often slips in unintended directions. RND’s intrinsic motivation is crucial here, encouraging systematic exploration of the larger grid world. The prediction error helps the agent discover safe paths through the expanded maze while understanding the stochastic nature of the environment, leading to robust policies that can navigate the complex 8x8 layout.en exploration in reinforcement learning.
Overview
Random Network Distillation (RND) is an exploration method that generates intrinsic rewards by measuring the agent’s ability to predict the output of a randomly initialized neural network. The key insight is that prediction error correlates with novelty - states that are visited less frequently are harder to predict, leading to higher intrinsic rewards and encouraging exploration.
Key features of this implementation:
- Intrinsic Motivation: Uses prediction error as curiosity signal
- PPO Integration: Combines RND with PPO for stable policy optimization
- Dual Advantage Estimation: Separate advantages for extrinsic and intrinsic rewards
- Normalization: Running normalization of intrinsic rewards for stable training
- Multi-Environment Support: Works with discrete and continuous control tasks
How RND Works
RND consists of two neural networks:
- Target Network: A randomly initialized network that remains fixed throughout training
- Predictor Network: A learnable network that tries to predict the target network’s output
The prediction error serves as an intrinsic reward:
intrinsic_reward = ||predictor(state) - target(state)||²
This encourages the agent to visit novel states where the prediction error is high.
Implementations
This repository includes multiple RND implementations:
Classic Control (train_classic.py)
- Environment: CartPole-v1
- Simple implementation for discrete action spaces
- Good starting point for understanding RND
Lunar Lander (lunar.py)
- Environment: LunarLander-v3
- Vectorized training with multiple parallel environments
- More complex continuous state space
- Optimized for performance and stability
Mountain Car (mountain-car.py)
- Environment: MountainCar-v0
- Sparse reward environment ideal for RND exploration
- Demonstrates RND’s effectiveness in hard exploration problems
Frozen Lake (lake.py)
- Environment: FrozenLake-v1 (8x8 map, 64 states)
- Discrete stochastic environment with slippery dynamics
- Demonstrates RND on larger discrete state spaces with one-hot encoding
Environments
This implementation has been tested on:
- CartPole-v1: Classic control task for balancing a pole on a cart
- LunarLander-v3: Spacecraft landing with continuous observations and discrete actions
- MountainCar-v0: Sparse reward environment where the agent must reach the mountain top
- FrozenLake-v1: Discrete 8x8 grid world (64 states) with stochastic slippery movement dynamics
Algorithm Details
RND + PPO Training Loop
- Environment Interaction: Collect trajectories using current policy
- Intrinsic Reward Calculation:
- Compute prediction error:
||predictor(state) - target(state)||² - Normalize intrinsic rewards using running statistics
- Compute prediction error:
- Advantage Estimation:
- Compute extrinsic advantages using environment rewards
- Compute intrinsic advantages using RND rewards
- Combine advantages with weighting coefficients
- Policy Update: Update policy using combined advantages via PPO
- Predictor Update: Train predictor network to minimize prediction error
Key Components
Target Network
class TargetNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_space):
super(TargetNet, self).__init__()
# Randomly initialized, never updated
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_space, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
Predictor Network
class PredictorNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_space):
super(PredictorNet, self).__init__()
# Learnable network
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_space, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
Configuration
Core Parameters
EXT_COEFF: Weight for extrinsic advantages (typically 1.0-2.0)INT_COEFF: Weight for intrinsic advantages (typically 0.5-1.0)lr: Learning rate for all networksgamma: Discount factor for returnsclip_value: PPO clipping parameter
RND-Specific Parameters
- Intrinsic Reward Normalization: Running mean and standard deviation
- Network Architecture: Hidden layer sizes for target and predictor networks
- Update Frequency: How often to update the predictor network
Results
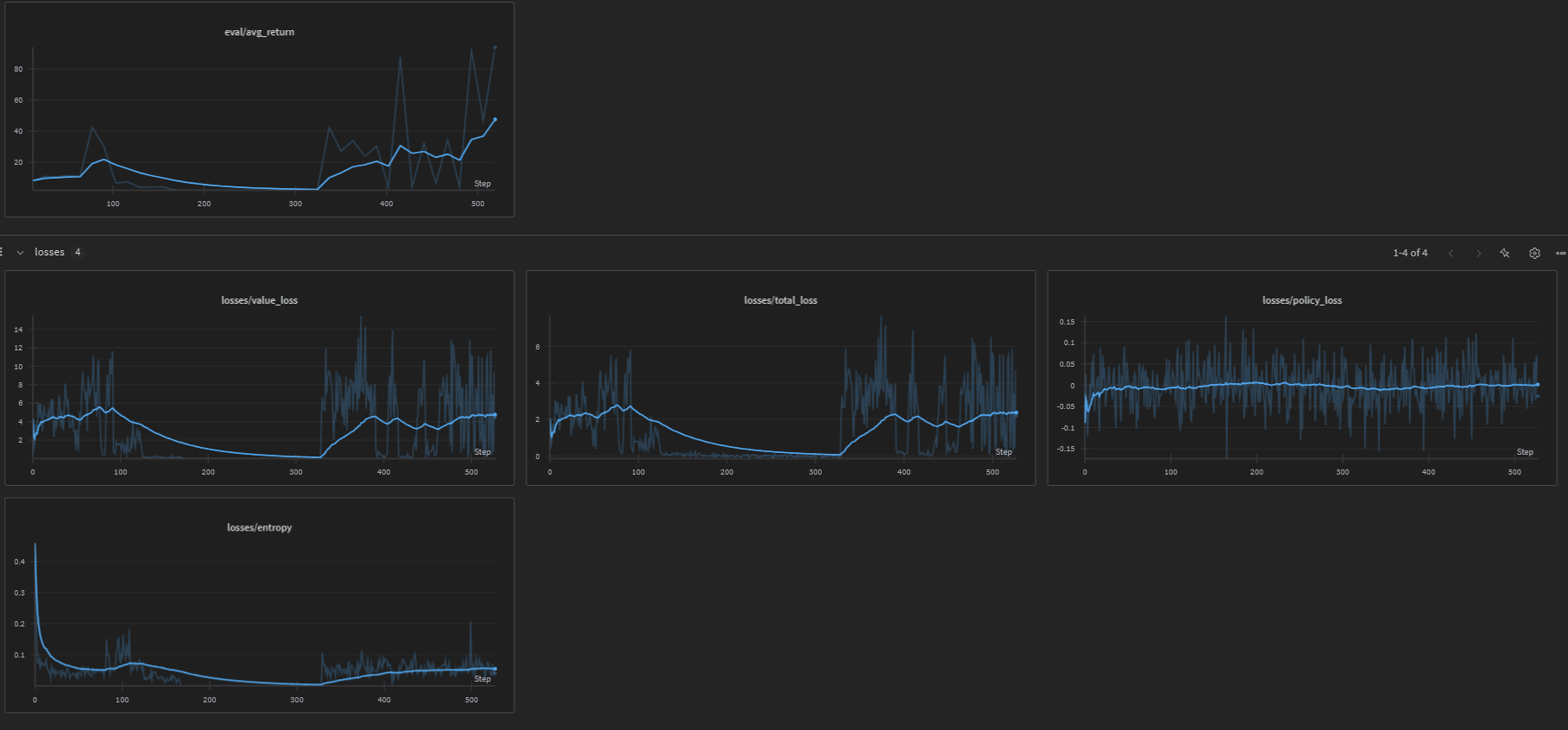
CartPole-v1
The following image shows the training performance on the CartPole environment with RND:
Agent gameplay demonstration:
Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: The results demonstrate that RND enables efficient exploration while successfully learning the main task. The agent learns to balance the pole while the intrinsic rewards encourage exploration of novel states.
LunarLander-v2
The following demonstrates RND performance on the more complex LunarLander environment:
Agent gameplay demonstration:
Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: In LunarLander, RND helps the agent explore different landing strategies and discover optimal trajectories while learning to land successfully. The intrinsic rewards encourage exploration of various parts of the landing zone.
MountainCar-v0
The following demonstrates RND performance on the challenging MountainCar environment with sparse rewards:
Agent gameplay demonstration:

Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: MountainCar is a particularly challenging environment for exploration due to its sparse reward structure. The agent only receives reward when reaching the goal at the mountain top. RND’s intrinsic motivation is crucial here, as it encourages the agent to explore different positions and velocities, eventually discovering the momentum-building strategy needed to reach the goal. The prediction error helps the agent explore novel state combinations that lead to successful mountain climbing.
FlappyBird
The following demonstrates RND performance on FlappyBird with curiosity-driven exploration:
Agent gameplay demonstration:
Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: In FlappyBird, RND encourages the agent to explore different flight patterns and obstacle navigation strategies. The intrinsic rewards help the agent discover diverse ways to navigate through pipes while learning the core task.
FrozenLake-v1
The following demonstrates RND performance on the stochastic FrozenLake environment:
Agent gameplay demonstration:

Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: FrozenLake is a challenging discrete environment with stochastic dynamics where the agent must navigate a slippery frozen lake to reach the goal while avoiding holes. RND’s intrinsic motivation is particularly valuable here as it encourages systematic exploration of the grid world. The prediction error helps the agent discover safe paths and understand the stochastic nature of the environment, leading to more robust policies that can handle the slippery dynamics.
CarRacing-v3
The following demonstrates RND performance with CNN on the challenging CarRacing environment:
Agent gameplay demonstration:
Detailed Training Metrics: View the complete training logs and metrics on Weights & Biases
Note: CarRacing is a complex continuous control environment with high-dimensional visual observations. RND with CNN architecture enables effective exploration of different racing strategies and track segments. The convolutional neural networks process the visual input while the intrinsic motivation from RND encourages the agent to explore diverse driving behaviors and track areas, leading to improved racing performance through curiosity-driven exploration.
Key Benefits of RND
- Simple Implementation: No need for complex count-based exploration
- Scalable: Works with high-dimensional state spaces
- Stable: Prediction error provides consistent exploration signal
- Task-Agnostic: Doesn’t require domain knowledge about the environment
Common Issues and Solutions
Intrinsic Reward Explosion
- Problem: Intrinsic rewards become too large, overwhelming extrinsic rewards
- Solution: Use running normalization and carefully tune
INT_COEFF
Insufficient Exploration
- Problem: Agent doesn’t explore enough novel states
- Solution: Increase
INT_COEFFor improve network architecture
Training Instability
- Problem: Training becomes unstable due to conflicting objectives
- Solution: Balance
EXT_COEFFandINT_COEFF, use smaller learning rates
Dependencies
- PyTorch
- Gymnasium
- NumPy
- WandB (optional, for experiment tracking)
- TensorBoard
- OpenCV (for video recording)
- Tqdm (for progress bars)
- ImageIO (for video saving)
References
- CleanRL: Implementation reference - Clean and simple RL implementations
Source Code
📁 GitHub Repository: RND (RND)
View the complete implementation, training scripts, and documentation on GitHub.
