Imitation Learning
Published:
Imitation Learning
Implementation of Imitation Learning reinforcement learning algorithm
Technical Details
- Framework: PyTorch
- Environment: Custom Environment
- Category: Imitation Learning
This project implements core Imitation Learning algorithms—including Behavioral Cloning (BC) and Dataset Aggregation (DAgger)—for learning policies from expert demonstrations in a GridWorld environment. The agent learns to imitate expert behavior by training a neural network to predict actions given states, and can further improve using interactive data collection (DAgger).
🎯 Overview
Imitation Learning is a family of techniques where agents learn to perform tasks by mimicking expert behavior. This project includes:
- Behavioral Cloning (BC): A supervised learning approach where a policy is trained on expert state-action pairs to directly imitate the expert.
- DAgger (Dataset Aggregation): An interactive algorithm that iteratively collects new data by letting the agent act and querying the expert for corrections, reducing compounding errors.
The learned policies can then be evaluated in the environment.
📁 Project Structure
├── BC.py # Behavioral Cloning implementation
├── DAgger.py # DAgger (Dataset Aggregation) implementation
├── gridworld.py # GridWorld environment
├── gridworld.json # Environment configuration
├── images/
│ └── image.png # GridWorld visualization
├── imitation-learning-tutorials/
│ ├── expert_data/
│ │ └── ckpt0.pkl # Expert demonstration data
│ └── ... # Additional tutorial notebooks
└── README.md # This file
🖼️ GridWorld Visualization
The GridWorld environment where the agent learns to navigate and imitate expert behavior.
🚀 Quick Start
Prerequisites
pip install torch tqdm wandb
Running the Code
Behavioral Cloning
python BC.py
This will:
- Load expert demonstrations from
expert_data/ckpt0.pkl - Train a policy network using behavioral cloning
- Evaluate the policy every 100 episodes
- Log training progress to Weights & Biases
DAgger
python DAgger.py
This will:
- Initialize with expert demonstrations
- Iteratively collect new data by running the agent and querying the expert
- Aggregate datasets and retrain the policy
- Evaluate and log progress
🧠 Model Architecture
PolicyNet
- Input: One-hot encoded state (2500 dimensions)
- Hidden Layers:
- FC1: 2500 → 128 (ReLU)
- FC2: 128 → 64 (ReLU)
- Output: 4 action logits (up, down, left, right)
Training Details
- Loss Function: Cross-entropy loss
- Optimizer: Adam (lr=2.5e-4)
- Batch Processing: Trains on individual expert episodes
📊 Monitoring with Weights & Biases
The code automatically logs:
- train_loss: Cross-entropy loss for each training episode
- eval_reward: Average reward during evaluation
- episode: Training episode number
- hyperparameters: Learning rate, architecture details
🔧 Configuration
Modify the Config class in BC.py:
@dataclass
class Config:
lr: float = 2.5e-4 # Learning rate
project_name: str = "behavioral-cloning" # WandB project name
run_name: str = "bc-gridworld" # WandB run name
📈 Key Components
BC Class
__init__(): Initializes policy network, optimizer, and WandB loggingtrain(): Trains on expert state-action pairs for one episodeevaluate(): Evaluates policy performance in the environment
DAgger Class
__init__(): Initializes policy, expert, and data bufferscollect_data(): Runs the current policy, queries expert for corrections, and aggregates new datatrain(): Retrains the policy on the aggregated datasetevaluate(): Evaluates policy performance in the environment
Plots
- BC and DAgger training losses and evaluation rewards are logged to Weights & Biases for visualization.
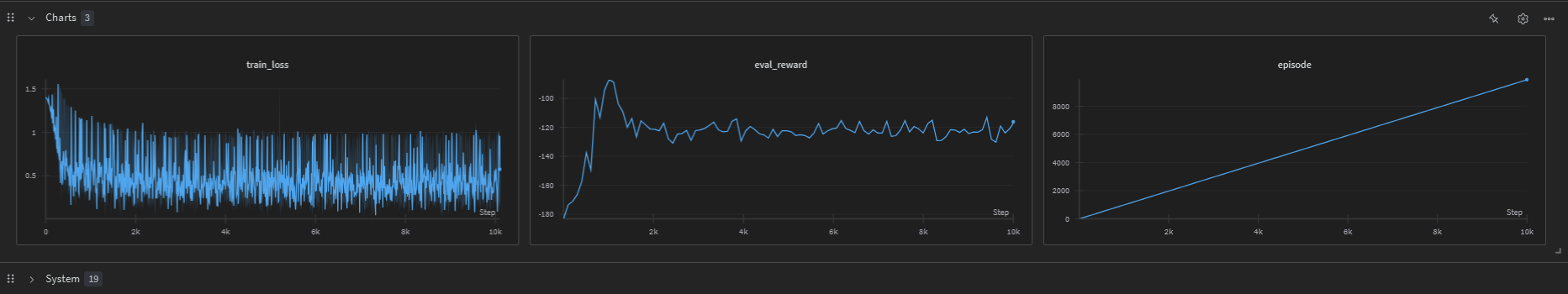
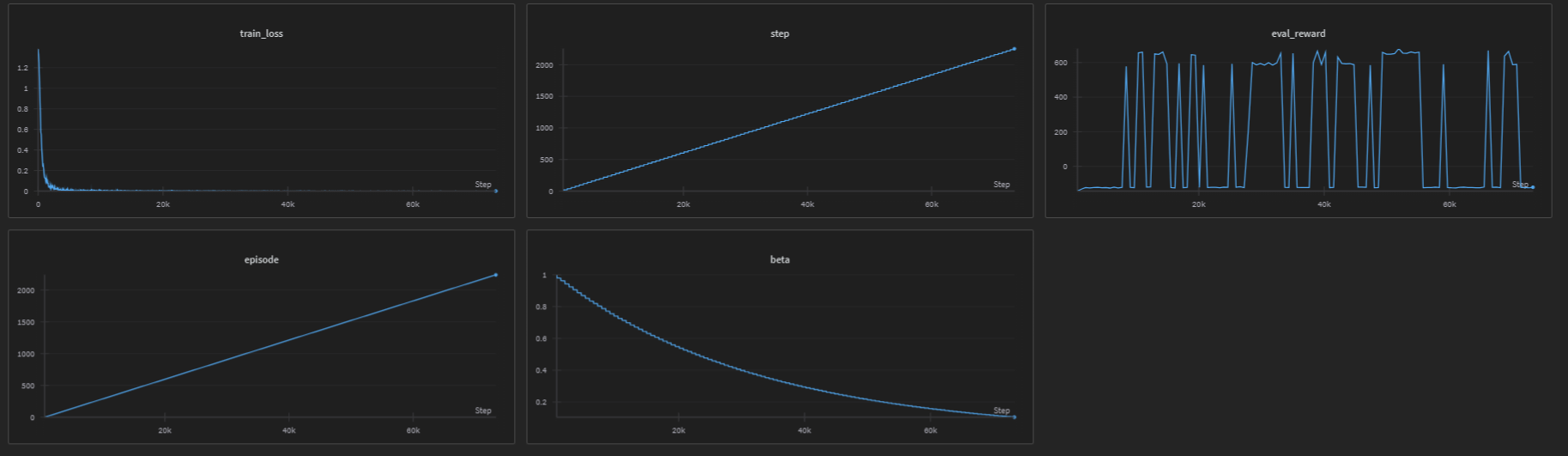
Helper Functions
sample_action(): Samples actions from policy logits (greedy/stochastic)one_hot_encode(): Converts state integers to one-hot vectors
BC Training Loop Example
curr = 0
for i, length in enumerate(timestep_lens):
# Extract episode data
expert_states = all_states[curr: curr + length]
expert_actions = all_actions[curr: curr + length]
# Train on this episode
loss = model.train(expert_states, expert_actions)
# Evaluate every 100 episodes
if i % 100 == 0:
rew = model.evaluate()
print(f"Episode {i}, Eval Reward: {rew}")
curr += length
DAgger Training Loop Example
for iteration in range(num_iterations):
# Collect data using current policy and expert
new_states, new_actions = model.collect_data()
# Aggregate with previous data
dataset.add(new_states, new_actions)
# Retrain policy
model.train(dataset.states, dataset.actions)
# Evaluate
if iteration % 5 == 0:
rew = model.evaluate()
print(f"DAgger Iteration {iteration}, Eval Reward: {rew}")
🎮 Environment Details
- GridWorld: 50x50 grid environment
- States: 2500 possible positions (50×50)
- Actions: 4 discrete actions (up, down, left, right)
- Evaluation: Uses batched environments (128 parallel instances)
📊 Expert Data Format
The expert data (ckpt0.pkl) contains:
states: Flattened array of all expert statesactions: Flattened array of all expert actionstimestep_lens: Length of each expert episode
🔍 Evaluation Metrics
- Average Reward: Mean reward per episode across evaluation runs
- Training Loss: Cross-entropy loss between predicted and expert actions
Note: Make sure to have expert demonstrations and proper environment setup before running the code.
Special Thanks: This implementation is inspired by the Imitation Learning tutorials available at Imitation Learning Tutorials
Source Code
📁 GitHub Repository: Imitation Learning (Imitation Learning)
View the complete implementation, training scripts, and documentation on GitHub.
